All things considered, Asian currencies have had an okay 2010 (and there’s still another month to go). After a modest first half, they started to rise in unison in June, and several are poised to finish the year 10% higher than where they began. While the last few weeks have seen a slight pullback, there is cause for cautious optimism in 2011.
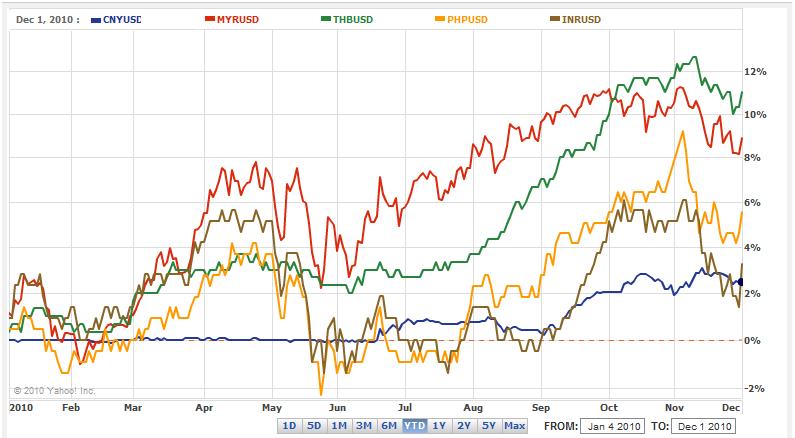
At this point, I think the rise in Asian currencies has become somewhat self-fulfilling. Basically, investors expect Asian currencies to rise, and the consequent anticipatory capital inflows cause them to actually rise, thereby reinforcing investor sentiment. For example, the co-head of emerging markets for Pacific Investment Management Company (PIMCO) is “investing in local currency debt and foreign exchange contracts in Asia on the basis that…emerging market currencies are bound to rise for…fundamental reasons.” Upon being asked to elaborate on such fundamentals, he answered lamely that, “One big driver for emerging markets in coming years will come from investors’ relatively low allocations to these fast-growing regions.”When pressed for actual reasons, investors can glibly rattle off such strengths as high growth and low debt and wax bullish about the emerging market ‘story,’ but ultimately they are chasing yield, asset appreciation, and strengthening exchange rates. It doesn’t matter that P/E ratios for (Asian) emerging market stocks are significantly higher than in industrialized economies, or that bond prices are destined to decline as soon as (Asian) emerging market Central Banks begin lifting interest rates, or that Purchase Power Parity (PPP) already suggests that some of these currencies are already fairly valued. In a nutshell, they continue to pour money into Asia because that’s what everyone else seems to be doing.
Personally, I think that kind of mentality should inspire caution in even the most bullish of investors. It suggests that if bubbles haven’t already formed in emerging markets, they probably will soon, since there’s no way that GDP growth will be large enough to absorb the continuous inflow of capital. According to the Financial Times, “Data suggest that emerging market mutual funds, including those invested in Asian markets, have received about 10 per cent of their assets in additional flows over the past four to five months.” Meanwhile, a not-insignificant portion of the $600 Billion Fed QE2 program could find its way into Asia, exacerbating this trend.
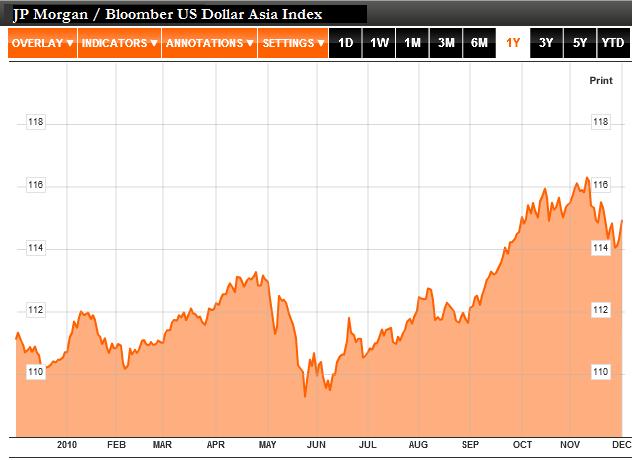
In addition, emerging markets in general, and Asia in particular, have always been vulnerable to sudden capital outflow caused by flareups in risk aversion. For example, Asian currencies as a whole (see the US Dollar Asian Currency Index chart above) have declined 2% in the month of November alone, due to interest rate hikes in China and a re-emergence of the EU sovereign debt crisis. The former sparked fears of a worldwide economic slowdown, while the latter precipitated a decline in risk appetite.As a bona fide fundamental analyst, it pains me to say that emerging market Asian currencies can expect some (modest) appreciation over the next year, barring any serious changes to the EU fiscal and global economic situations. It seems that capital will continue to pour into Asia, which – rather than fundamentals – will continue to dictate performance.

At this point, I think the rise in Asian currencies has become somewhat self-fulfilling. Basically, investors expect Asian currencies to rise, and the consequent anticipatory capital inflows cause them to actually rise, thereby reinforcing investor sentiment. For example, the co-head of emerging markets for Pacific Investment Management Company (PIMCO) is “investing in local currency debt and foreign exchange contracts in Asia on the basis that…emerging market currencies are bound to rise for…fundamental reasons.” Upon being asked to elaborate on such fundamentals, he answered lamely that, “One big driver for emerging markets in coming years will come from investors’ relatively low allocations to these fast-growing regions.”
Personally, I think that kind of mentality should inspire caution in even the most bullish of investors. It suggests that if bubbles haven’t already formed in emerging markets, they probably will soon, since there’s no way that GDP growth will be large enough to absorb the continuous inflow of capital. According to the Financial Times, “Data suggest that emerging market mutual funds, including those invested in Asian markets, have received about 10 per cent of their assets in additional flows over the past four to five months.” Meanwhile, a not-insignificant portion of the $600 Billion Fed QE2 program could find its way into Asia, exacerbating this trend.

In addition, emerging markets in general, and Asia in particular, have always been vulnerable to sudden capital outflow caused by flareups in risk aversion. For example, Asian currencies as a whole (see the US Dollar Asian Currency Index chart above) have declined 2% in the month of November alone, due to interest rate hikes in China and a re-emergence of the EU sovereign debt crisis. The former sparked fears of a worldwide economic slowdown, while the latter precipitated a decline in risk appetite.
No comments:
Post a Comment